Product Information
Talk about hope in propolis.
Talk about hope in propolis.
Propolis is a powerful defense system produced nature.
Propolis is a natural sticky substance collected
by honeybees(Apismellifera L.) from the buds
of numerous plant species, depending on the climate zone.
Propolis is normally utilized in the hive to coat the inner walls,
to shelter from the entrance of intruders,
such as snakes and lizards, or against wind and rain, and to prevent fungi and bacteria growth.

Propolis is resin from conifer buds and other trees
that honeybees use to seal walls,
strengthen the honeycombs, and embalm intruders in the hive.
The precise composition of propolis varies with the source,
and over 300 chemical components belonging to the flavonoids, terpenes, and phenolic acids have been identified in propolis.
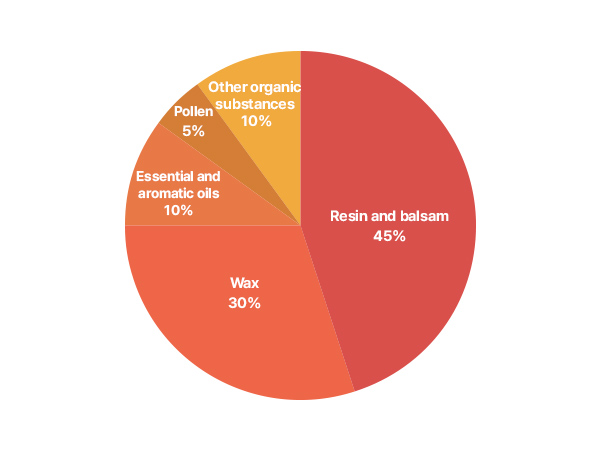
Propolis’ main components are: 1. Resin and balsam (45%),
2. Wax (30%), 3. Essential and aromatic oils (10%)
4. Pollen (5%), 5. Other organic substances (10%)
Depending on where the honeybees live,
the composition of the propolis will change as a function
of different environments and ecosystems.
For example, propolis from Europe and Asia won’t have
the same chemical makeup as propolis from Brazil.

Asian and European propolis contain the typical ‘poplar
bud’ phenolics: flavonoid aglycones (flavones and flavanones),
phenolic acids and their esters. Poplar trees are common only in the temperate zone; they cannot grow in tropical
and subtropical regions (such as Brazil or Argentina).
For this reason, bees have to find other plant sources
of propolis to replace the poplar trees.
As a result, propolis from tropical and subtropical regions has
a different chemical composition from that of poplar type propolis.

The main source of Brazilian propolis turned out
to be the leaf resin of Baccharis dracunculifolia.
In contrast to Asian and European propolis,
among the main compound classes found
in Brazilian propolis are prenylated derivatives
of p-coumaric acid and of acetophenone.
Diterpenes, lignans and flavonoids (different from those
in ‘poplar type’ propolis), and artepillin C have also been found
in Brazilian green propolis.
| Active Compounds | Functional Properties |
|---|---|
| Artepillin C | Anti-inflammatory, Anti-tumor, Anti-oxidation |
| Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester | Immunomodulating, Anti-virus, Anti-tumor, Anti-inflammatory |
| Cinnamic acid | Anti-oxidation, Anti-bacterial, Anti-tumor |
| ρ-Coumaric acid | Anti-oxidation |
| Chrysin | Anti-inflammatory |
| Kaempferol | Antihyperglycemic, Anti-oxidation |
| Pinocembrin | Anti-bacterial, Anti-inflammatory, Anti-oxidation |
| β-amyrin | Anti-tumor, Anti-inflammatory |